
JavaScript ES6 語法糖 - 解構賦值介紹
前言:
解構賦值 ( Destructuring Assignment)是一個在 ES6 的新特性,目的用於提取陣列或物件中的資料變成獨立變數。
引用 從ES6開始的JavaScript學習生活 中的英文說明如下:
The Destructuring Assignment syntax is a JavaScript expression that makes it possible to extract data from arrays or objects using a syntax that
mirrors the construction of array and object literals
這句後面的 mirrors the construction of array and object literals,代表這個語法的使用方式 - 如同鏡子一般,對映出陣列或物件字面的結構。也就是一種樣式(pattern)對映的語法。
引用卡斯伯老師說的白話文:
會將右方的資料往左邊送,然後會一個位置對一個值 (但沒有像鏡子左右顛倒)。
陣列解構賦值方法(Array Destructuring)
過去陣列內的元素在賦值的時候,只能透過直接給值的方式,像是下面這樣:
let list = [a, b];
let a = list[0];
let b = list[1];
console.log(a, b) //a,b而在 ES6 世界中,我們可以這樣用,而這就是最基本陣列解構賦值方法
備註:解構賦值會將右方的資料往左邊送,然後會一個位置對一個值
第一種
let [a, b, c] = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(a, b, c) //1,2,3
變數 a = 1, b = 2, c = 3
第二種寫法
let number = [1, 2, 3];
let [andy, chunwen , jay] = number;
console.log(andy, chunwen, jay) //[1, 2, 3]接著,我們開始來看不同案例摟~
情況一:當輸入變數多於所給的值
let [a , b, c, d] = [1, 2, 3]
console.log(a, b, c, d) // 1,2,3, undefined
情況二:當輸入變數少於所給的值
let [a, , c, d] = [1, 2, 3, 4]
console.log(a, c, d) //1,3,4
情況三:陣列解構中賦予預設值
let [a, b, c = 4, d = 'Hi'] = [1, 2, 3];
console.log(a, b, c, d); // 1, 2, 3, "Hi"
說明:因為 c 後面已經有給值,所以輸出結果一樣為3。而 d 在後面沒有給值,就直接帶入了預設值,得到 "Hi"。
情況四:字串拆解
let str = '我好帥氣喔';
let [a, b, c, d] = str;
console.log(a, b, c, d); //我 好 帥 氣
情況五:交換以下兩個變數
let Kaohsiung = '高雄';
let Taipei = '台北';
[Kaohsiung, Taipei]=[Taipei, Kaohsiung];
console.log(Kaohsiung, Taipei)
//台北 高雄,解構賦值是從右到左物件解構賦值
首先,必須強調一個觀念。物件的解構賦值強調的是屬性名稱,屬性名稱必須相互對應才能取到值,反之則會無法取值
基本方法如下:
物件解構 // 請取出物件內的兩個值到單一變數上
let family = {
ming: '小明',
jay: '杰倫',
};
let familyAll = { ...family }
console.log(familyAll); //{ming: "小明", jay: "杰倫"}
let obj = {
website: "pjchender",
country: "Taiwan"
}
let { website, country} = obj;
console.log( website ); // pjchender
console.log( country ); // Taiwan而上面寫法其實是縮寫,下面寫法才是完整寫法let { website : website , country : country } = obj;
物件解構賦值原理如下:
它會根據前面的屬性名稱來對應要給的值,但值其實是給冒號(:)後面的變數,用圖來看像是這樣子: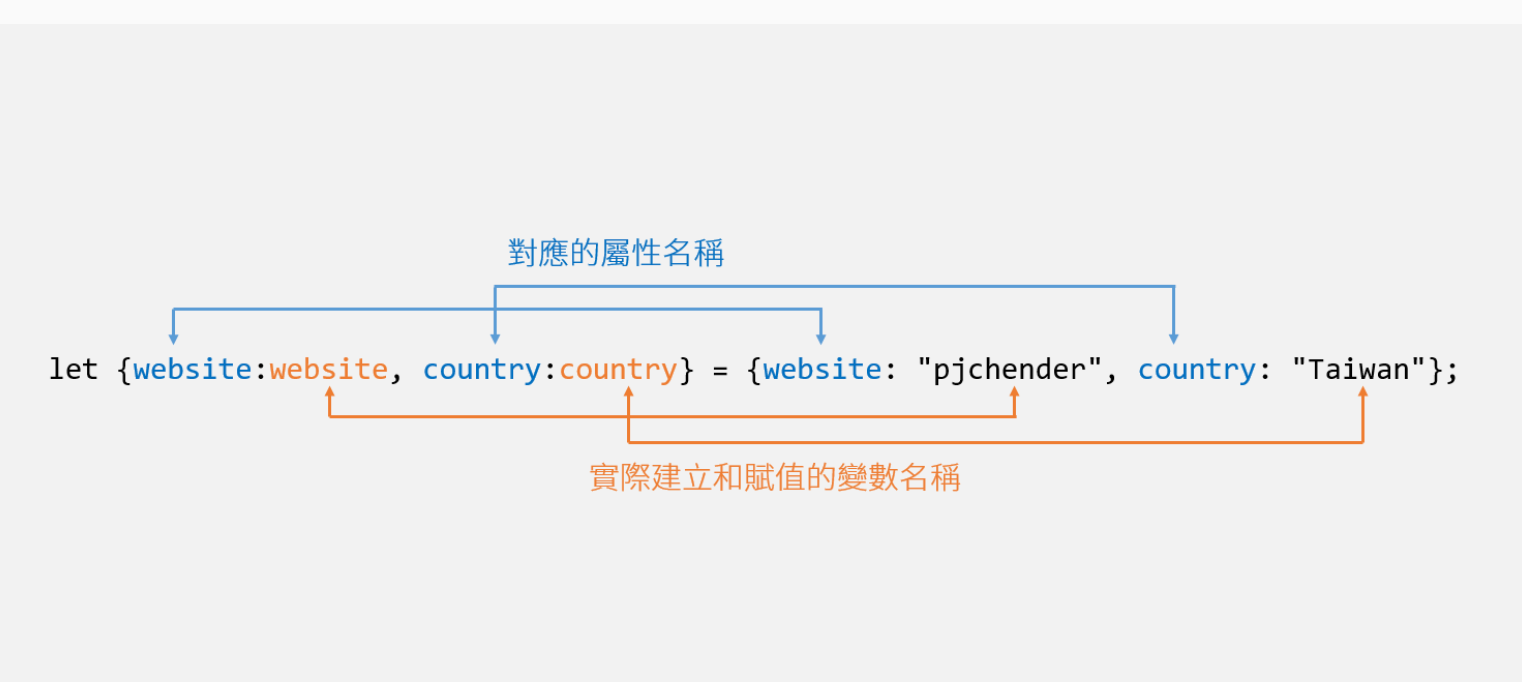
圖片來源:PJChender 部落格
接著,我們了解觀念後再來看一個例子:
let GinyuTeam = {
Ginyu: '基紐',
Jeice: '吉斯',
burter: '巴特',
}
let{ Ginyu : andy, Jeice : candy } = GinyuTeam;
console.log( Ginyu , Jeice ); //Ginyu is not defined
console.log( andy , candy );// 基紐 吉斯
說明:我們從這個例子,可以發現只有 andy, candy 這兩個變數會回傳正確值。也就是說,在物件解構賦值中,冒號前是用來對應物件的屬性名稱,冒號後才是真正建立的變數名稱和被賦值的對象。
相對的,當冒號前的屬性名稱對應不到物件中的屬性名稱時,則會出現 undefined。
test 和 Ginyu 屬性名並沒有相對應
let{test} = {Ginyu: "基紐"};
console.log(test); // undefined物件解構賦值其他例子
情境一:預設值
// 第一個會被賦值,第二個會用預設(由右至左賦值)
let [ming = '小明', jay = '杰倫'] = ['阿明']
console.log(ming, jay); //阿明 杰倫
let { family : ming = '小明' } = {}
console.log( ming ) //小明
情境二:物件解構
// 請取出物件內的兩個值到單一變數上
let family = {
ming: '小明',
jay: '杰倫',
};
let familyAll = { ...family }
console.log(familyAll); //{ ming: "小明", jay: "杰倫"}結論
陣列的解構賦值強調的是順序,而物件的解構賦值強調的則是屬性名稱,屬性名稱必須相互對應才能夠取得到值
 標籤雲
標籤雲 文章列表
文章列表